A pre engineered buildings is a metal structure that comprises light check metal standing crease rooftop boards on steel purlins. Steel Purlins span between rigid frames with light gauge metal wall cladding. It has a relatively more flexible structure than a conventional steel-framed building. All in all, it has a lot more notes a worthy vertical, and even diversion.
Pre Engineered Buildings concepts are widely used in many industrialized countries. It consists of complete steel frame building systems, with components pre-designed to fit together. It has a variety of combinations to meet the specific requirements of end users.
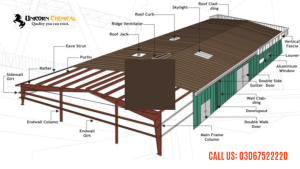
Different Parts Assemble in the development of Pre-Engineered Buildings
- Eave Strut
- Roof Panel
- Roof Purlin
- Rigid Frame rafter
- Ridge Line
- End Wall
- Wall Panel
- Side Wall
- Rigid Frame Column
- Downspout
- Gutter
- Ridge Panel
- Cable Bracing
Typical Pre Engineered Building Parts Assembling
The rigid frame assembly is the most well-known outline utilized in pre-designed structures. The rigid frame consists of a structural steel (hot rolled) moment resisting column and beam assembly that carries the cold form roof purlins and wall girts.
In addition, diagonal road bracing is required in the walls to resist horizontal loading on the building. Rod bracing is also provided within the roof framing to resist racking and twisting of the building.

Terminologies of Pre Engineered Buildings
Base Plate
A plate is attached to the base of a column that rests on the foundation. It is usually secured by anchor bolts.
Butt Plate
The end plate of a structural member is usually used to rest against a like plate of another member forming a connection. Now and then called a split plate or darted end plate.
Bay
The space between outline focus lines or essential supporting individuals in the longitudinal bearing of the structure.
Brace Rods
Bars or links are utilized in rooftops and walls to move loads, for example, wind loads and seismic and crane pushes to the establishment. Likewise, frequently used to plumb structures, yet not intended to supplant erection links.
Clear Height
This is the distance between the Finished Floor Level to the bottom of the knee joint.
Roof Slope
This is the point of the rooftop with the regard to the flat. The most widely recognized rooftop slants are 0.5/10 and 1/10. Any practical roof slope is possible.
Types of Framing System
1. Mezzanine Flooring through Pre Engineered Buildings

2. North Light
3. Monitor Type
4. Canopy

Advantages of Pre Engineered Buildings
Fast Project Construction
- Structures are created and conveyed inside a brief period because of normalization.
- Quick Erection since all individuals are field blasted.
Pre Engineered Buildings are Functionally Versatile
- Modular Construction
- Large Clear Spans (Up to 100m)
- Long Bay Spacing (Up to 13m)
- Structures are effectively expandable on all sides (considering future development).
Architectural Flexibility
- Stylish Features like belts, railings, and bended overhang significantly work on the presence of the structure.
- Promptly accessible point of interaction subtleties among steel and different materials (coating, block wall, drapery wall, and so on).
Low Maintenance and Operating Cost
- Virtually no maintenace required to all panels
- Roof requires only periodic cleaning.
- Annual Washing of Eave gutters.
- Watertight Roofs.
Disadvantages of Pre Engineered Buildings
- Relatively Short Life Span.
- Sometimes has an “industrial” or “warehouse” look to it.
- The foundation system is not design by a manufacturer.
- On location adjustment in design isn’t possible.
Applications of Pre Engineered Buildings
- Commercial Buildings
- Auditorium & Halls
- Administration Buildings














Leave A Comment